Add Jobs to Workflows
After adding a step, let's move on to a workflow job. This will be a basic job that will perform a transformation on the coordinates of point(s) you place on the map in the first spatial input step, using the numbers you add in the second step in the table input. Those transformations will be displayed on a map in the next step.
Start from Previous Solution
If you wish to use the previous solution as a starting point:
git clone https://github.com/Aquaveo/tethysapp-workflows_tutorial.git
cd tethysapp-workflows_tutorial
git checkout -b add-workflow-step-step add-workflow-step-step-complete
Job Executables
Begin by adding the following code to your app.py file. We'll need this to find where our job scripts are stored.
...
import os
class App(TethysAppBase):
...
@classmethod
def get_job_executables_dir(cls):
"""
Returns:
str: the path to the directory containing the job executables.
"""
return os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'job_executables')
Next, we'll need a jobs.py file:
Add a file named jobs.py to your basic_workflow folder with these contents:
from pathlib import Path
from ..utilities import safe_str, get_condor_env
REQUEST_CPUS_PER_JOB = 1
JOB_EXECUTABLES_DIR = Path(__file__).parent / 'job_executables'
def build_jobs_callback(condor_workflow):
"""
Define the Condor Jobs for the run step.
Returns:
list<dicts>: Condor Job dicts, one for each job.
"""
jobs = []
condor_env = get_condor_env()
workflow = condor_workflow.tethys_workflow
# Get the selected scenarios
points_step = workflow.get_step_by_name('Point In Boundary Step')
points_geometry = points_step.get_parameter('geometry')
# Create one job per point
for idx, point in enumerate(points_geometry.get('features', [])):
# Set up the job for the generic job
executable = 'run_generic_job.py'
point_name = point.get('properties', {}).get('point_name', f'point_{idx + 1}')
job_name = f'run_{safe_str(point_name)}'
output_filename = f'{job_name}_out.json'
job = {
'name': job_name,
'condorpy_template_name': 'vanilla_transfer_files',
'category': 'generic_job',
'remote_input_files': [str(JOB_EXECUTABLES_DIR / executable), ],
'attributes': {
'executable': executable,
'arguments': [point_name, idx, output_filename],
'transfer_input_files': [f'../{executable}', ],
'transfer_output_files': [output_filename, ],
'environment': condor_env,
'request_cpus': REQUEST_CPUS_PER_JOB
}
}
# Add to workflow jobs
jobs.append(job)
return jobs
Next, add a folder called job_executables in your basic_workflow folder. This folder will hold the scripts that get run as part of our jobs.
The first file you'll add to this new folder will be called run_generic_job.py, with the following contents:
#!/opt/tethys-python
import json
from pprint import pprint
from shapely.geometry import Point, Polygon
from tethysext.workflows.services.workflows.decorators import workflow_step_job
@workflow_step_job
def main(
db_session, workflow, step, gs_private_url, gs_public_url, workflow_class,
params_json, params_file, cmd_args, extra_args
):
# Extract extra args
point_name = extra_args[0]
output_filename = extra_args[2]
print("Params JSON: ", params_json)
boundary_points = params_json['Boundary Input Step']['parameters']['geometry']['features'][0]['geometry']['coordinates'][0]
boundary_polygon = Polygon(boundary_points)
print(f"\n\n\nBoundary Points: {boundary_points}\n\n\n")
# Find the point id and original point coordinates from the Point In Boundary Step
features = params_json['Point In Boundary Step']['parameters']['geometry']['features']
for feature in features:
if feature['properties']['point_name'] == point_name:
print(f"\n\n\nFeature: {feature}\n\n\n")
point_id = feature['properties']['id']
original_point_coordinates = feature['geometry']['coordinates']
# Get the transformations for the point from the Spatial Dataset Step
transformations = params_json['Spatial Dataset Step']['parameters']['datasets'][point_id]
print("Transformations: ", transformations)
print(f'Running job for point: {point_name}')
x = [original_point_coordinates[0]]
y = [original_point_coordinates[1]]
# Apply the transformations to the point and check if each new point is within the boundary
for index in range(len(transformations['X'])):
new_coords = [original_point_coordinates[0] + float(transformations['X'][index]), original_point_coordinates[1] + float(transformations['Y'][index])]
if boundary_polygon.contains(Point(new_coords)):
x.append(new_coords[0])
y.append(new_coords[1])
# Create the series data
series = {
'name': point_name,
'x': x,
'y': y,
}
print('Results:')
pprint(series, compact=True)
# Save to file
print('Saving File... ')
with open(output_filename, 'w') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(series))
print('Saved file Successfully')
This script will do a few things. First, it will pull the transformation data assigned to each of the point(s) you've placed on the map and transform the original coordinates of each point with that data. It will then make sure that those new coordinates are inside the boundary you've placed on the map in the first step. You'll add those points to a map in the next step of this tutorial.
Lastly, add the following step to your workflow code:
from ..workflow_base import WorkflowBase
from tethysext.workflows.steps import SpatialInputStep, SpatialDatasetStep, TableInputStep, FormInputStep, SetStatusStep, JobStep
from .attributes import PointAttributes
from .jobs import build_jobs_callback
import pandas as pd
Class BasicWorkflow(WorkflowBase):
...
execute_step = JobStep(
name='Run Job Step',
order=70,
help='Review input and then press the Run button to run the workflow. '
'Press Next after the execution completes to continue.',
options={
'scheduler': app.SCHEDULER_NAME,
'jobs': build_jobs_callback,
'working_message': 'Please wait for the execution to finish running before proceeding.',
'error_message': 'An error occurred with the run. Please adjust your input and try running again.',
'pending_message': 'Please run the workflow to continue.'
},
geoserver_name=geoserver_name,
map_manager=map_manager,
spatial_manager=spatial_manager,
)
workflow.steps.append(execute_step)
return workflow
Refresh your app, and create a new workflow. Complete the first step, and hit "Next". You'll see the map with the point you've selected. Click "Run", and you'll see this:
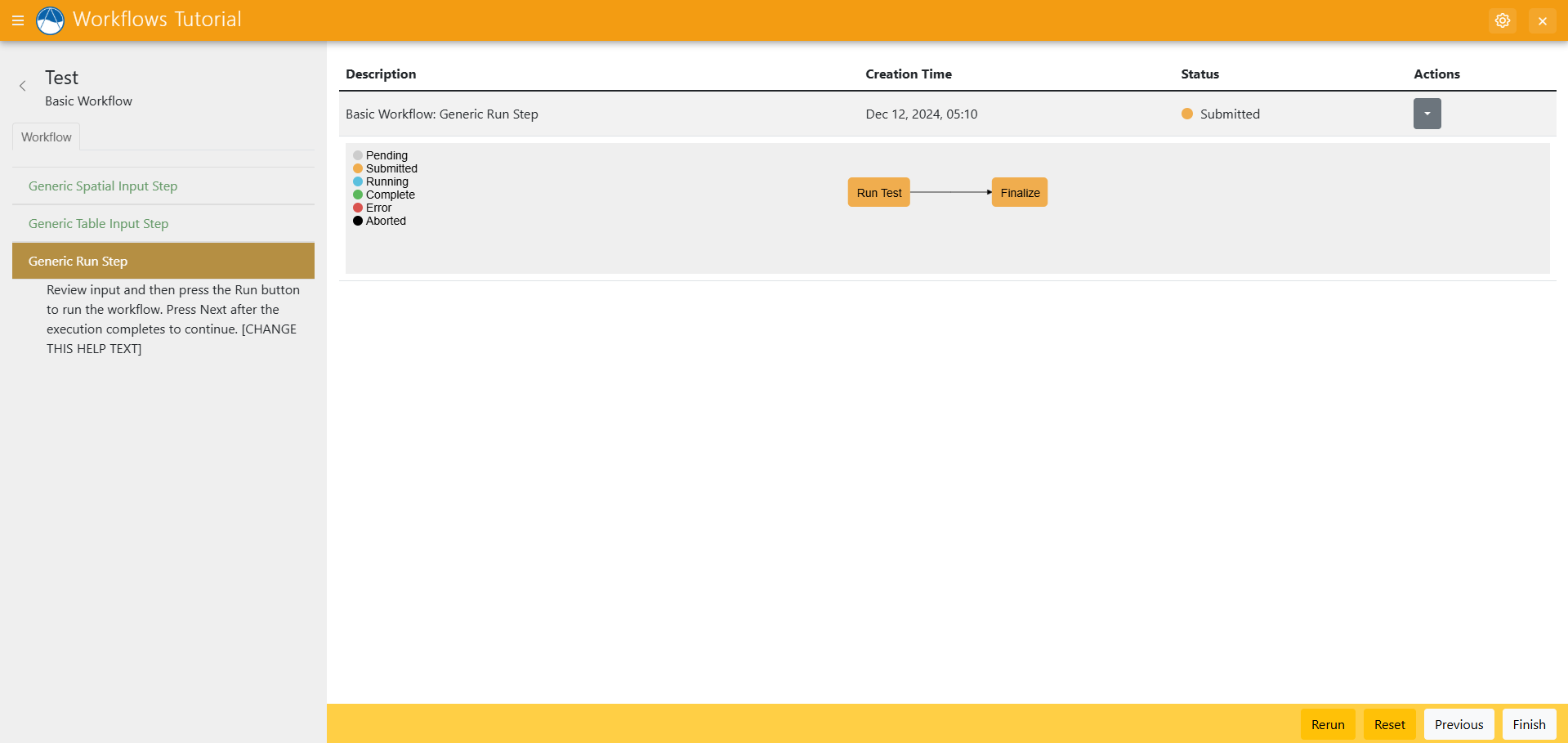
Wait for the job to finish running.
You should find a folder called workspaces/userworkspaces/your_username Inside that folder you'll find a new folder with a random set of characters for the name. Inside you'll find the out.json file with your job's results. Those results will be the original coordinates of the original point, along with the new transformed coordinates that are inside the boundaries you've chosen. In the next step, you'll visualize those results, along with other data from your workflow.
Solution
This concludes the Add Jobs portion of the Tethys Workflows Extension Tutorial. You can view the solution on GitHub at https://github.com/Aquaveo/tethysapp-workflows_tutorial or clone it as follows:
git clone https://github.com/Aquaveo/tethysapp-workflows_tutorial.git
cd tethysapp-workflows_tutorial
git checkout -b add-job-step add-job-step-complete